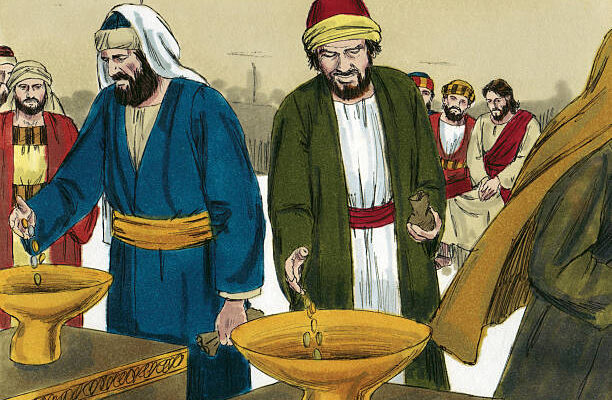
Sacrifice has been an integral aspect of religious practices across cultures and civilizations throughout human history. The act of sacrificing, whether through rituals, offerings, or personal commitments, holds a profound significance in various religious traditions. It is a symbolic gesture that transcends the material realm, embodying devotion, faith, and the willingness to surrender for a higher purpose. This article explores the importance of sacrifice in religious practices, delving into its spiritual, cultural, and communal dimensions.
Historical Perspectives on Sacrifice
 (Photo from iStock)
(Photo from iStock)
To comprehend the importance of sacrifice in religious practices, it is essential to examine its historical roots. The concept of sacrifice dates back to ancient civilizations, where various cultures engaged in rituals to appease deities, seek favour, or maintain cosmic balance. In ancient Mesopotamia, for instance, the practice of sacrificing animals was common in religious ceremonies, signifying a connection between the earthly and divine realms.
The Romans, too, had elaborate rituals involving sacrifices to honour their pantheon of gods. Similarly, in ancient Indian religions, sacrificial ceremonies known as yajnas played a crucial role in Vedic traditions, emphasizing cosmic order and divine harmony.
Religious Sacrifice as a Symbol of Devotion
 (Photo from iStock)
(Photo from iStock)
In Christianity, the concept of sacrifice is central to the faith, with the ultimate sacrifice being the crucifixion of Jesus Christ. This act is considered an atonement for human sins, illustrating God’s love for humanity and the willingness to sacrifice his own son for the salvation of mankind.
In Islam, sacrifice is a fundamental component of the annual festival of Eid al-Adha, commemorating the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God. The festival emphasizes the importance of submission to the divine will and the significance of sacrifice in expressing one’s faith.
Hinduism, with its diverse array of deities and rituals, places a strong emphasis on sacrificial acts. Yajnas, fire rituals performed with specific chants and offerings, are believed to create a spiritual connection between the worshipper and the divine forces. These rituals symbolize the cyclical nature of creation, preservation, and destruction, reinforcing the interconnectedness of all life.
Sacrifice in Judaism is deeply rooted in the narrative of the Hebrew Bible, where offerings such as burnt sacrifices were made to God as expressions of gratitude, repentance, or seeking divine favour. The concept of sacrifice is intricately woven into the fabric of Jewish identity, reflecting a covenant between God and the chosen people.
Symbolism and Spiritual Transformation
 (Photo from iStock)
(Photo from iStock)
Sacrifice in religious practices goes beyond the mere physical act of offering. It carries profound symbolic meaning, often representing spiritual transformation and purification. In many traditions, the act of sacrificing is viewed as a means of shedding the ego, overcoming material attachments, and aligning oneself with higher spiritual truths.
The act of giving up something valuable symbolizes a renunciation of worldly desires and a commitment to a higher, spiritual purpose. This symbolic gesture becomes a transformative experience for the individual, fostering a deeper connection with the divine and promoting inner growth.
In the context of Christianity, the Eucharist, or Holy Communion, is a symbolic act of sacrifice where believers partake in the body and blood of Christ. This ritual signifies a spiritual union with Jesus and a commemoration of his sacrifice on the cross. The symbolism in the breaking of bread and sharing of wine underscores the profound connection between the individual and the divine.
One of the paths to spiritual realization outlined in ancient scriptures. Eventually, karma yoga advocates performing one’s duties selflessly, without attachment to the fruits of one’s actions.
Community and Communal Bonds
 (Photo from iStock)
(Photo from iStock)
Sacrifice in religious practices often extends beyond individual acts of devotion to foster a sense of community and communal bonds. Rituals and ceremonies involving sacrifice bring people together. Further, creating a shared experience that strengthens the fabric of religious communities.
In Judaism, the Passover sacrifice and communal meals during festivals like Hanukkah and Sukkot. Serve as occasions for families and communities to come together. These shared rituals reinforce a sense of identity, continuity, and solidarity among the Jewish people.
In Islam, the annual Hajj pilgrimage and the sacrifice of animals during Eid al-Adha exemplify communal worship. And unity among Muslims worldwide.
In Hinduism, festivals such as Diwali involve communal rituals and the exchange of offerings. Furthermore, fostering a sense of togetherness and shared spirituality. The celebration of Navaratri, marked by communal dances and worship, exemplifies the collective nature of religious practices in Hindu culture.
Ethical Dimensions of Sacrifice
 (Photo from iStock)
(Photo from iStock)
Beyond its spiritual and communal aspects, sacrifice in religious practices often carries ethical dimensions. The act of sacrificing is not only about giving up something valuable. But, also about making choices aligned with moral principles and ethical conduct.
While traditional sacrificial rituals involving animals are not central to Buddhist practice. Moreover, the idea of sacrificing one’s ego and self-centred desires is fundamental. The path to enlightenment involves the renunciation of attachment and the cultivation of compassion for all sentient beings.
In Sikhism, the concept of sacrifice is embodied in the principles of seva (selfless service) and simran (remembrance of God).
Conclusion
The importance of sacrifice in religious practices transcends cultural, historical, and doctrinal boundaries. Whether expressed through rituals, offerings. Or personal commitments, the act of sacrificing holds profound significance in fostering spiritual growth. Building communal bonds, and reinforcing ethical values.
Sacrifice is a symbolic language that communicates devotion, submission, and a willingness to transcend the self for a higher purpose. Evidently, embodies the universal human yearning for connection with the divine and the recognition of something greater than oneself. In a world marked by diverse religious traditions. The concept of sacrifice remains a timeless and powerful force that continues to shape the spiritual landscape of humanity. This way we can get knowledge of several scarifies that are in different religions in the world.




